Obsidian Thin Section

Obsidian is extremely rich in silica about 65 to 80 is low in water and has a chemical composition similar to rhyolite.
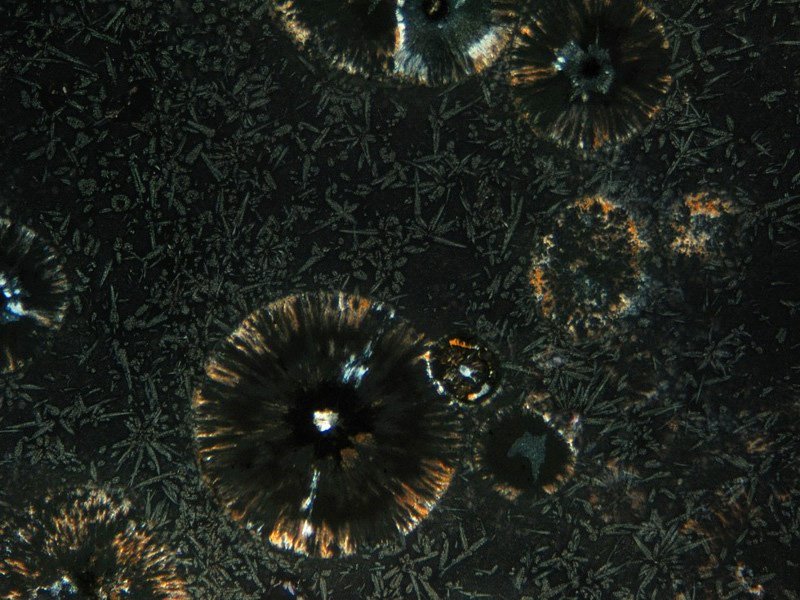
Obsidian thin section. Most obsidian is associated with volcanic rocks and forms the upper portion of rhyolitic lava flows. Obsidian has a glassy lustre and is slightly harder than window glass. Having familiarized ourselves with the general outward appearance of the rock forming obsidian cliff let us look deeper into the subject and by means of the microscope penetrate to the very heart of the matter.
The obsidians of mount hekla in iceland the eolie islands off the coast of italy and obsidian cliff in yellowstone national park wyoming u s are all well known occurrences. Obsidian is much denser than pumice. Obsidian obsidian is a igneous rock occurring as a natural glass formed by the rapid cooling of viscous lava from volcanoes.
In thin section it is clear that the rock is not pure glass but a fine grained matrix of glass and randomly oriented feldspar laths less than 50 microns long. The cooling of lava takes place so rapidly that no chance remains for proper crystallization atomic arrangements and finds as an amorphous glass material. Obsidian is a class of igneous rocks which forms when felsic lava extruded from a volcano onto the surface of the earth.
The second is a thin section rock description where you have a slice of the rock which is on a glass slide making it possible to view the rock under a microscope. There are two different types of rock description which either may be done together or separately. It occurs less abundantly as thin edges of dikes and sills.
.jpg)




.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
