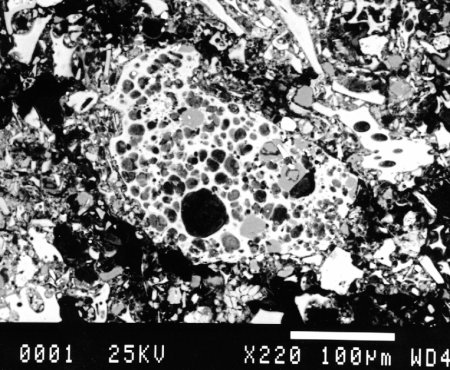
Pumice Thin Section

Minerals present differing amounts in differing sections.
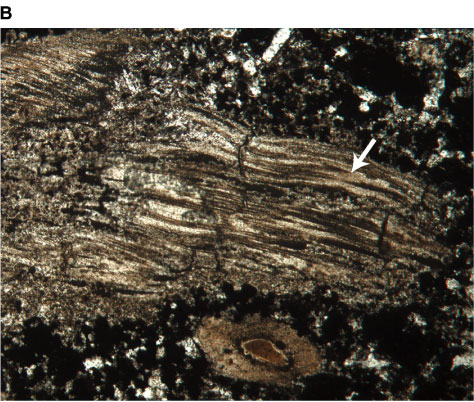
Pumice thin section. The glass colorless to light brown and hard to see with all the air bubbles entrained in the epoxy bubbles in epoxy have thin birefringent rims. After reviewing the textures and mineralogy decide which process it has undergone. Most of the thin clasts are pumice blocks that collapsed and flattened as they were reheated.
This outcrop is along the resting springs pass near death valley ca. Go back to igneous rocks page. The porous nature of pumice occurs because of simultaneous rapid cooling and rapid depressurization.
It is typically light colored. Plane cross polarized light field width is 3 mm. There are several phenocrysts of brown to green pyroxene magnetite and plagioclase.
The ash pumice and clasts were so hot that they remelted to form a glassy rock after landing on the ground. Large amounts of pumice produced by some island and subsea eruptions will float on the surface and be pushed about by the winds. Pumice made of about 90 gas bubbles.
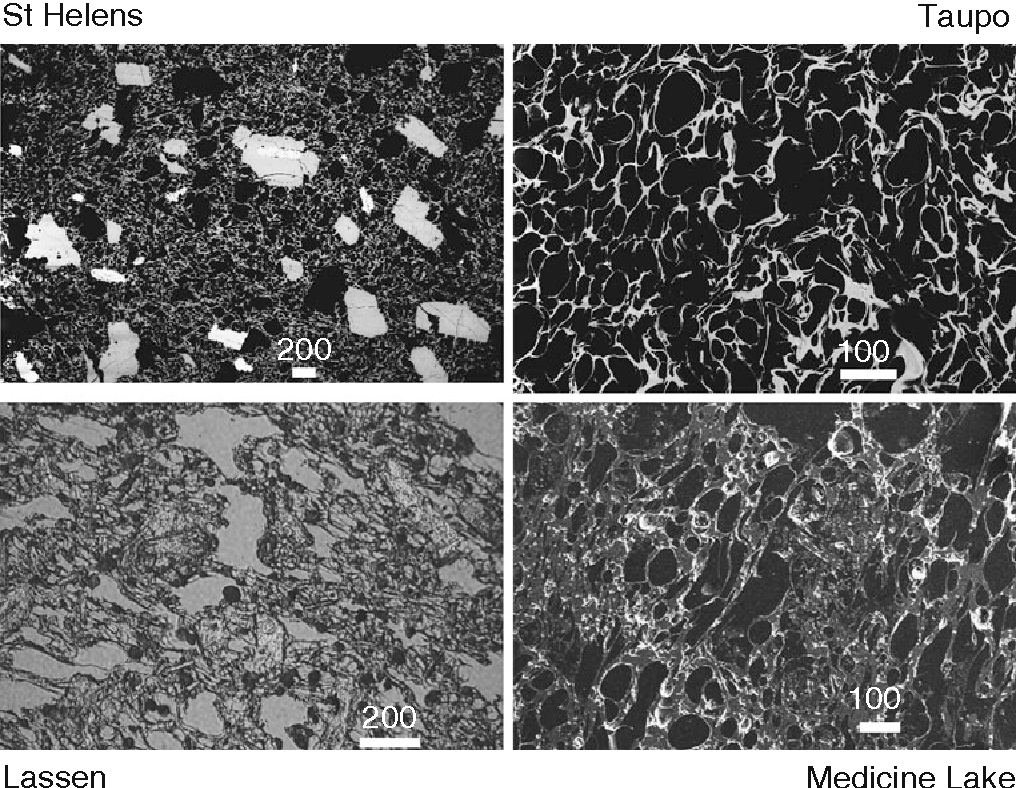
Pumice forms when super heated highly pressurised lava is violently ejected from a volcano. The abundant vesicles in pumice and the thin walls between them give the rock a very low specific gravity. Pumice is a volcanic rock that consists of highly vesicular rough textured volcanic glass which may or may not contain crystals.
Pumice thin section slide exhibiting the highly vesicular nature of this extrusive igneous rock. Scoria is another vesicular volcanic rock that differs from pumice in having larger vesicles and thicker vesicle walls and being dark colored and denser.









.jpg)

(6).jpg)



