Why Are Histological Sections Stained

The tissue is usually sectioned on a cryostat or freezing microtome.
Why are histological sections stained. Because there is no differentiation step background staining can occur especially with charged or treated slides. You observe a tissue that has cells of varying heights. This makes the tissue hard and much easier to cut sections from.
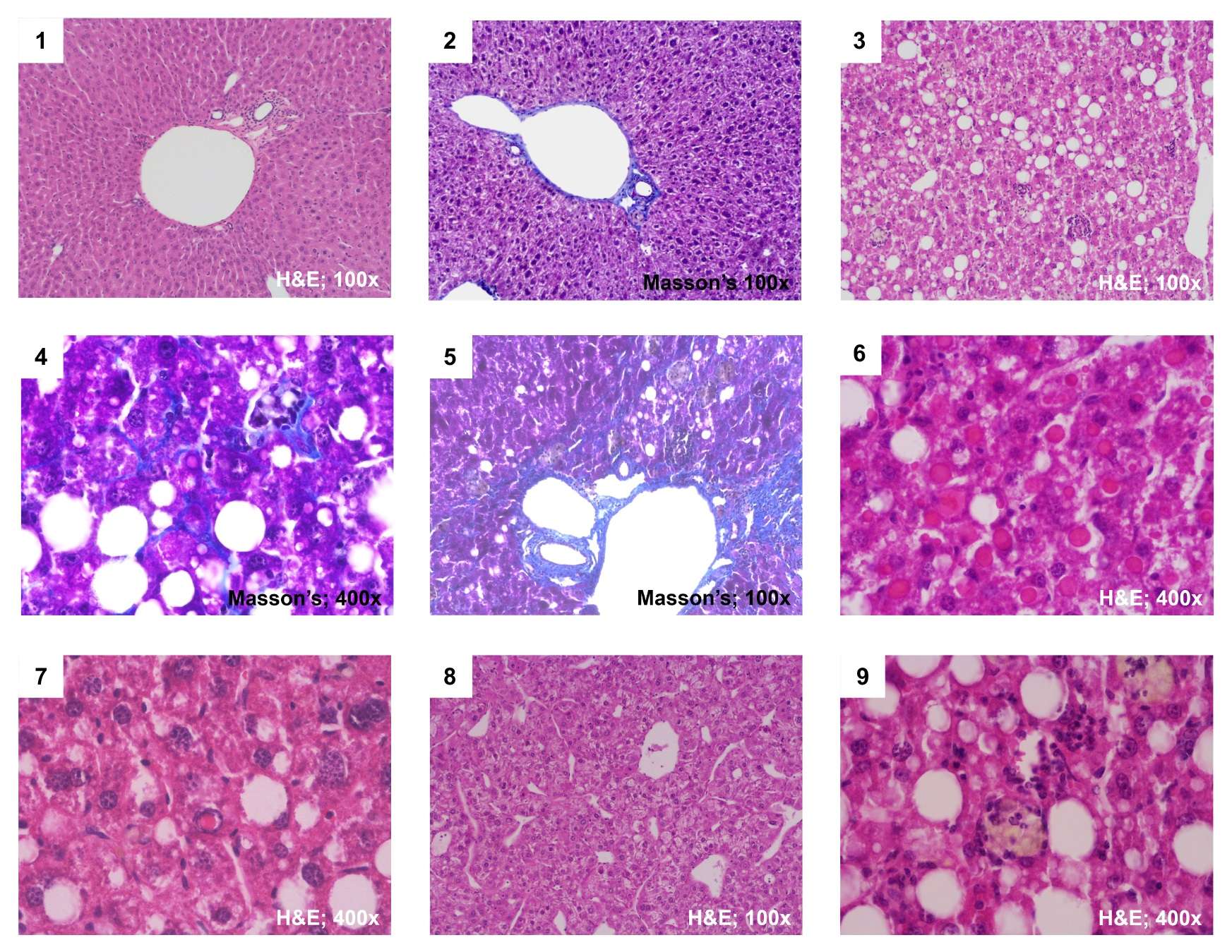
Histopathology refers to the study of tissues that are abnormal or diseased. Histology refers to the study of the individual parts and structures which make up a cell and the relationship between structure and function. The frozen sections are mounted on a glass slide and may be stained to enhance the contrast between different tissues.
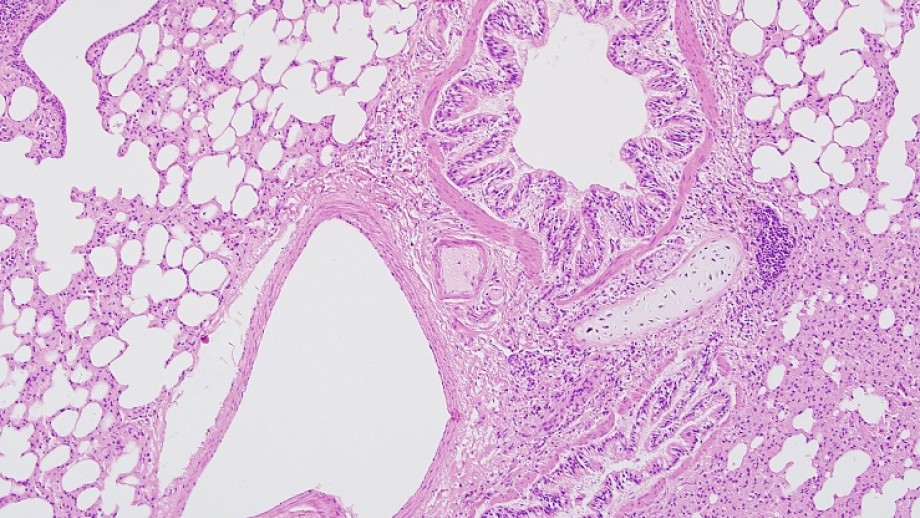
Polarity is a property of all normal epithelial tissues. For staining paraffin sections of tissue are normally used. Sections are then stained and examined with the light microscope.
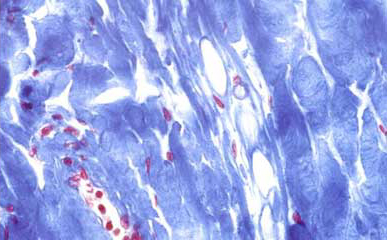
At first glance it appears that the. Pathologists sometimes prefer this type of stain because the non cellular material such as mucin becomes stained with the hematoxylin. This extracellular staining can be an indicator of well differentiated tumors.
Histochemical stains typically haematoxylin and eosin are therefore used to provide contrast to tissue sections making tissue structures more visible and easier to evaluate. Histological sections are stained to enhance the visualization and differentiation of microscopic structures. The role of microvilli is to.
Certain stains change the coloration of cells and tissues significantly different from the color of the original dye complex a phenomenon known as metachromasia. Epithelial tissues are innervated and usually vascularized. Histology stains are used to colour different structures within the cells.